A scar is a permanent mark on the skin that forms after a wound or surgery heals. They can be atrophic (depressed), hypertrophic (raised), or keloids (fibrous growths).
Types of scars:
- Atrophic scars: Acne, chickenpox, stretch marks
- Hypertrophic scars: Surgery, burns
- Keloid scars: Genetic predisposition, deep wounds
Different treatment options:
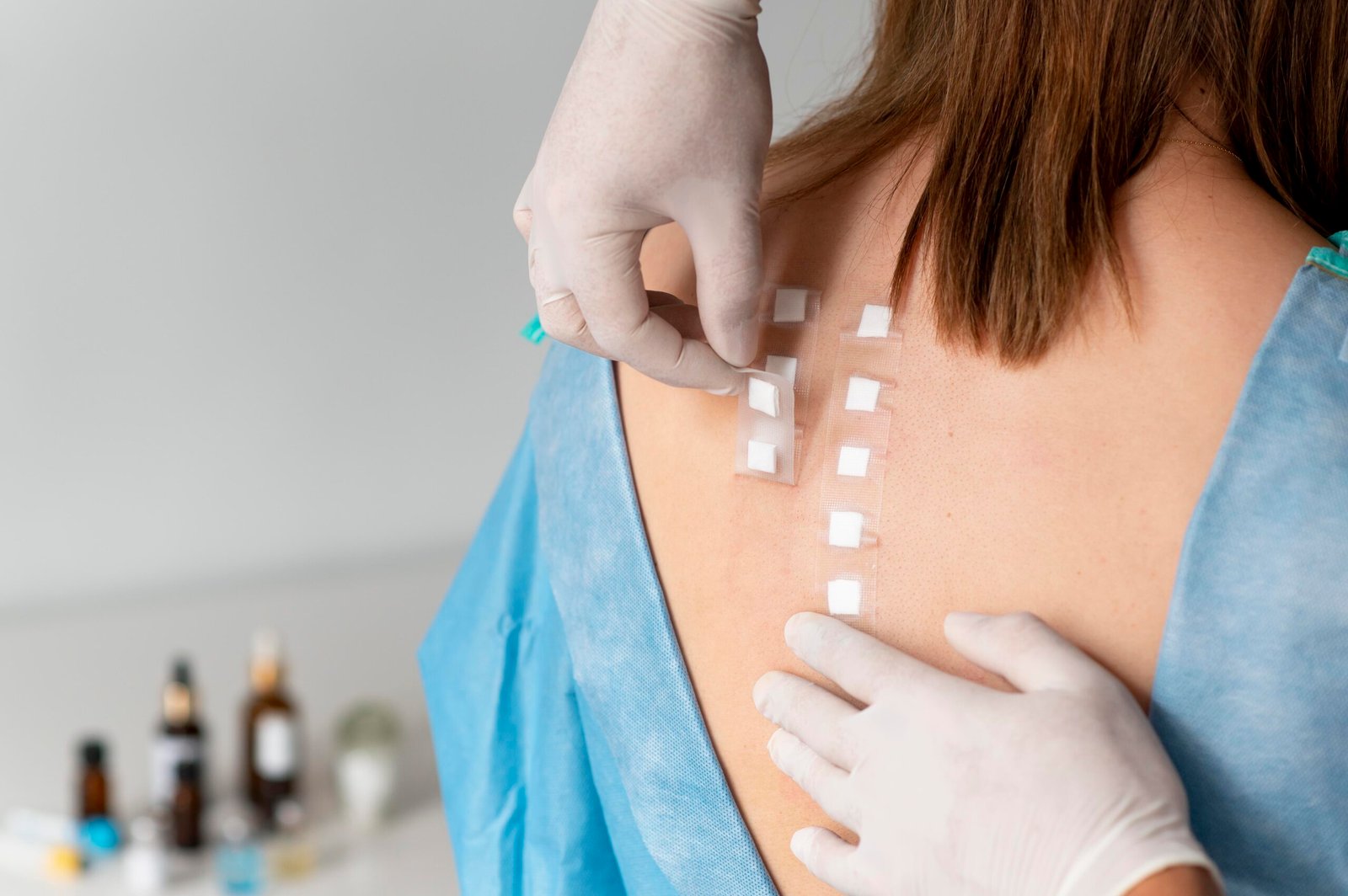
- Topical treatments: Creams, gels, patches with silicone, acids, or natural extracts
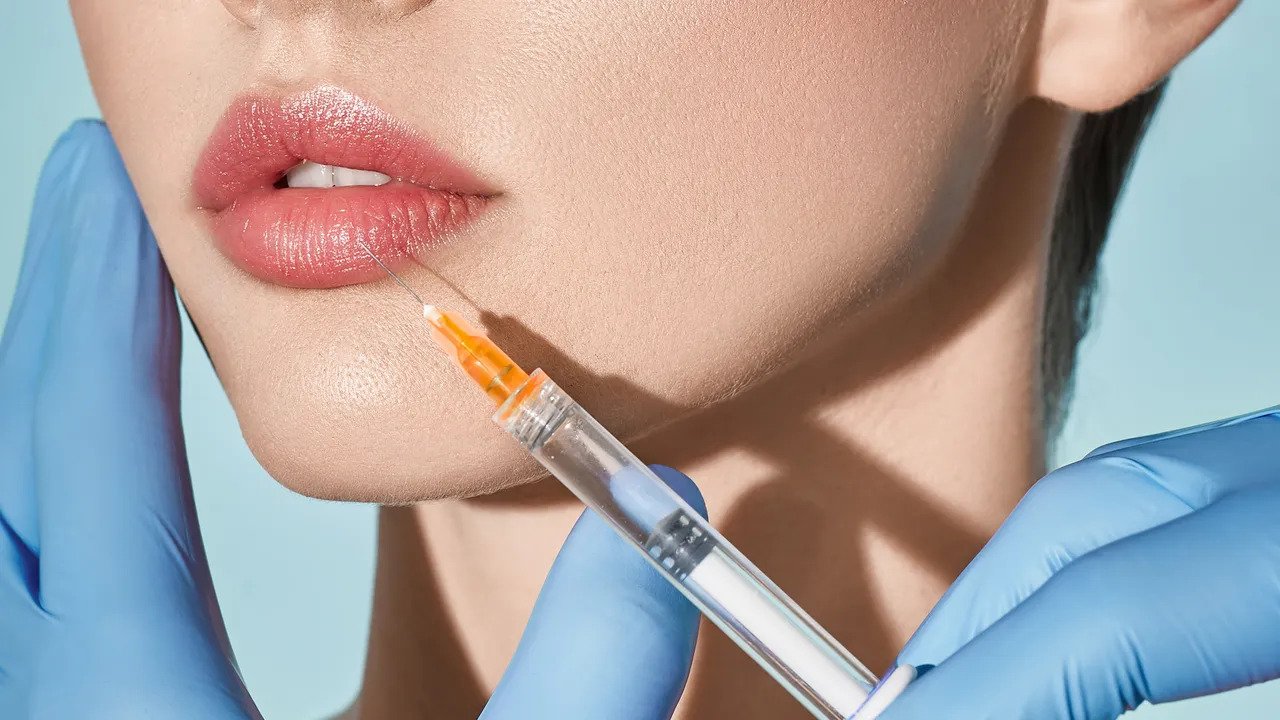
- Injections: Cortisone, hyaluronic acid
- Physical therapies: Laser, intense pulsed light, radiofrequency, dermabrasion, chemical peel
- Surgery: Scar revision, excision
Treatment selection:
The choice of treatment depends on the type of scar, its size, location, and the patient’s age.
Treatment goals:
- Improve the appearance of the scar
- Reduce pain and itching
- Improve skin texture and color
- Regain smooth and even skin
Variable results:
The effectiveness of treatments varies and results are never guaranteed. It is important to have realistic expectations.
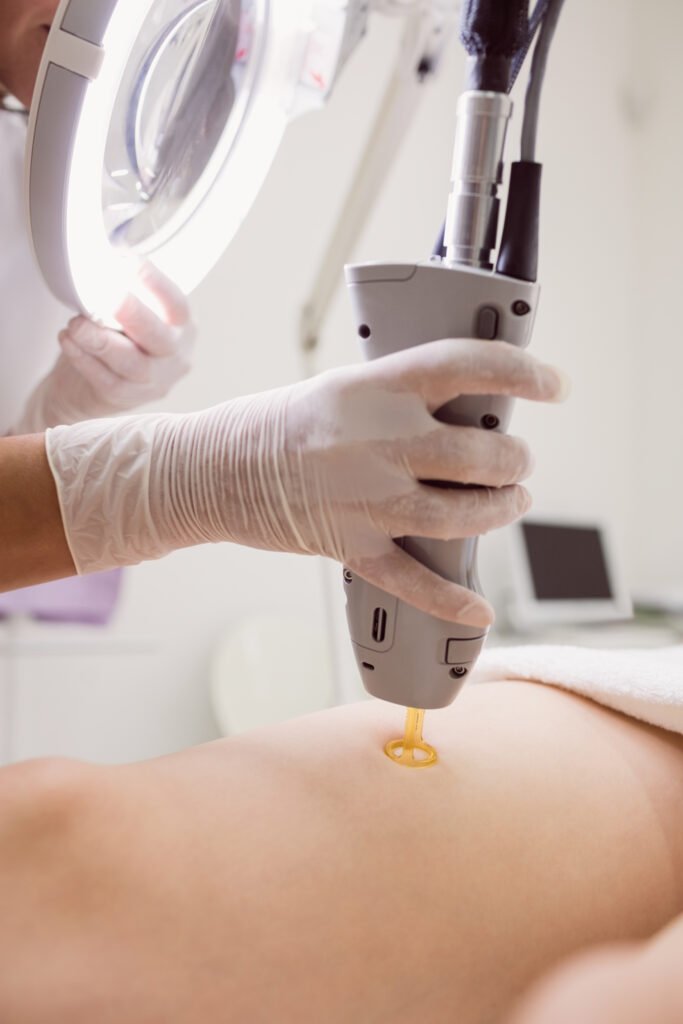
Tips for preventing scars:
- Keep the wound clean and protected
- Avoid scratching the scab
- Apply sunscreen to the scar
- Consult a dermatologist for unsightly scars
There are many options for treating scars and improving their appearance. A dermatologist can help you choose the most suitable treatment for your case.





























Name*
katana