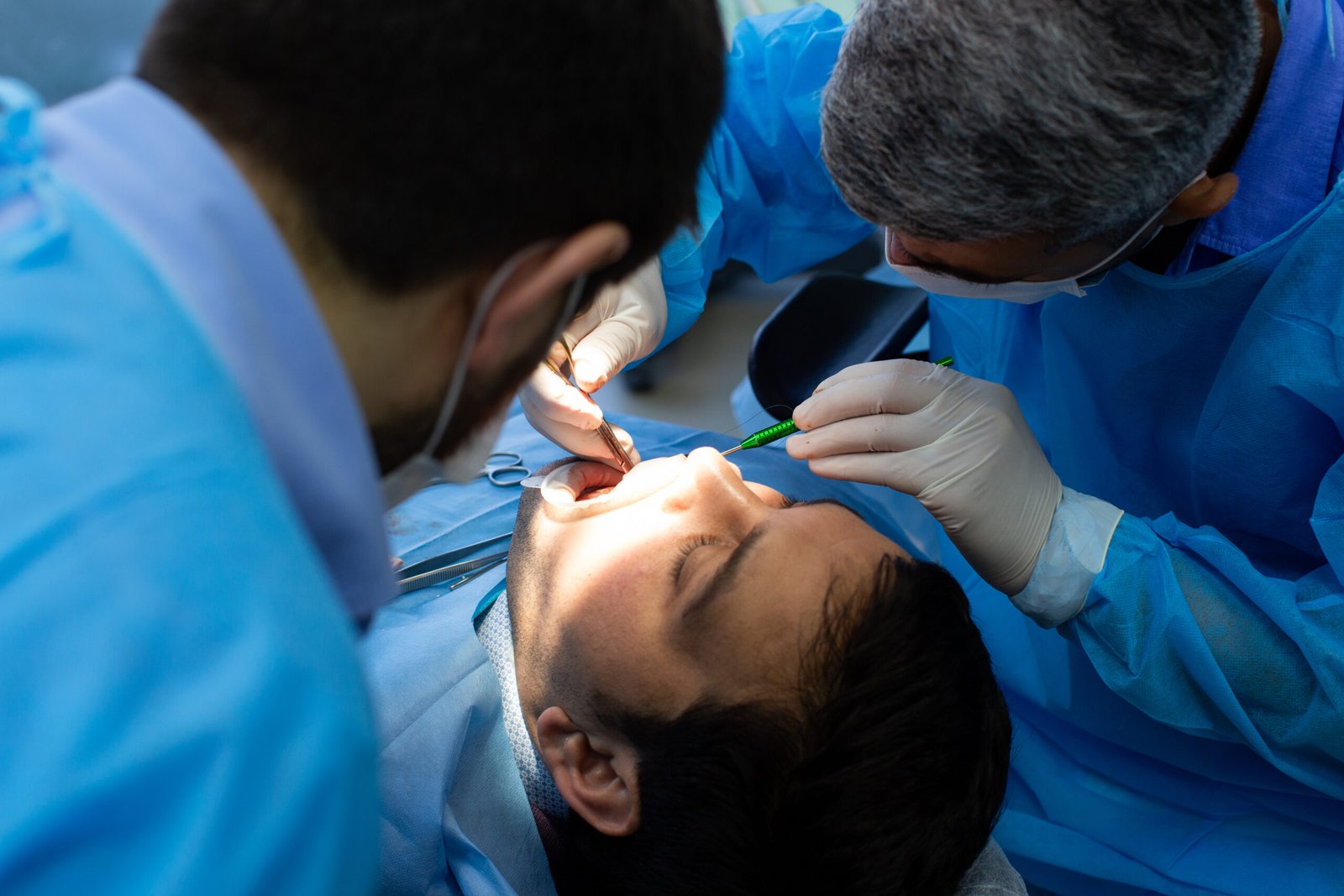
Jaw reconstruction, also known as orthognathic surgery, is a surgical procedure that aims to correct bone deformities of the upper and/or lower jaw. It restores masticatory function, facial harmony, and the patient’s quality of life.
Various Pathologies and Surgical Solutions:
Pathologies:
- Malocclusion: Misalignment of teeth and jaws.
- Prognathism: Lower jaw is too far forward.
- Retrognathism: Lower jaw is too far back.
- Facial asymmetry: Differences in size or position between the jaws.
- Mandibular atrophy: Decrease in bone mass of the jaw.
Surgical solutions:
- Osteotomy: Cutting and repositioning of the jaw bones.
- Advancement or setback of the jaw: Modification of the jaw position.
- Genioplasty: Modification of the chin shape.
- Distraction osteogenesis: Lengthening of the jaw.
- Bone grafting: Adding bone mass to fill a defect.
Anesthesia and Type of Procedure:
The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia and takes between 1 and 4 hours, depending on the complexity of the case.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care:
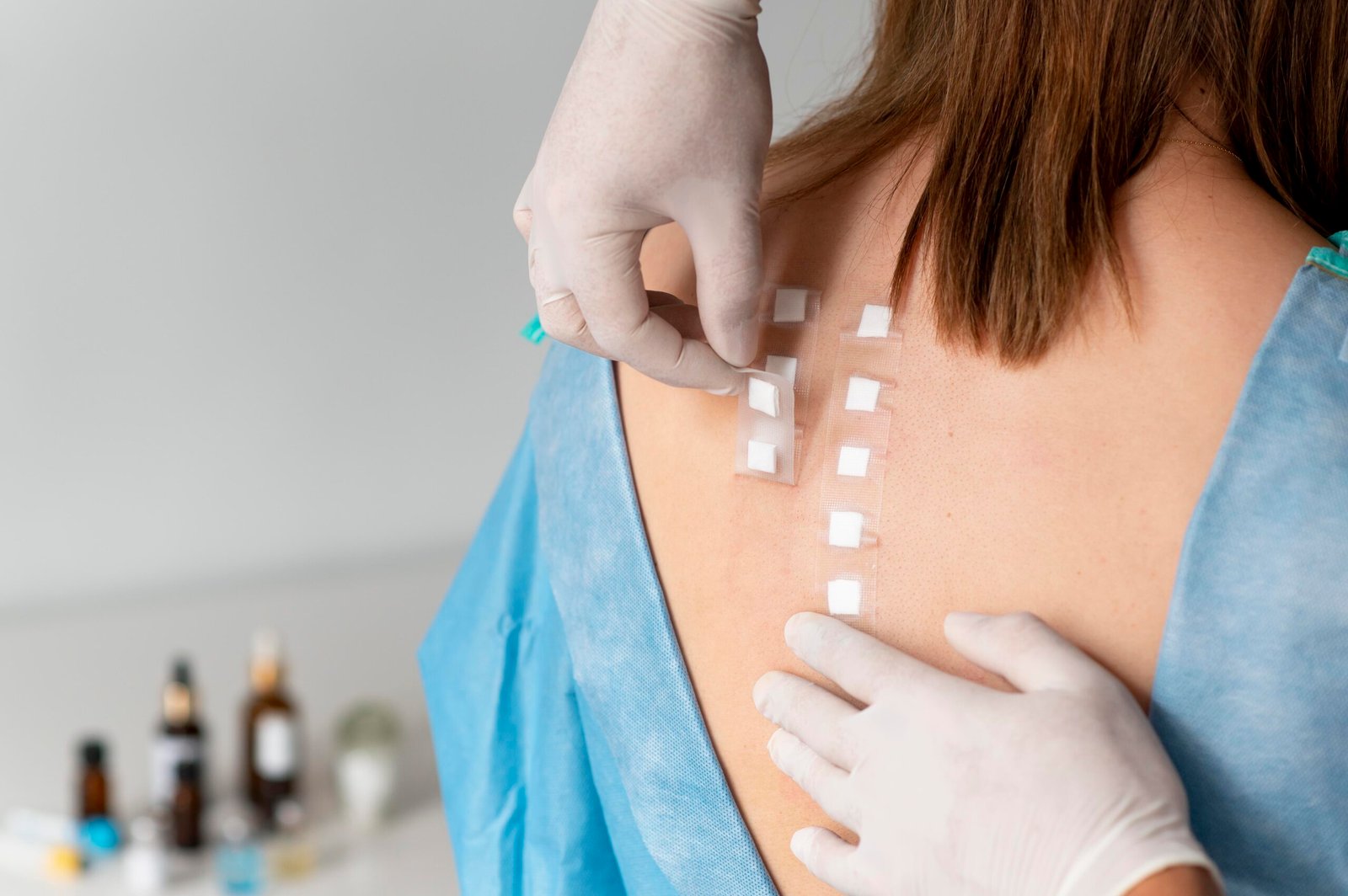
Recovery varies and requires wearing a bandage and a liquid or semi-liquid diet for several weeks. Pain, bruising, and swelling may occur, but they gradually disappear.
Long-Lasting Results and Improved Quality of Life:
Jaw reconstruction can achieve a long-lasting result, better masticatory function, corrected dental occlusion, restored facial harmony, and improved self-esteem.

Who Is It For?
Jaw reconstruction is an option for patients with:
- Jaw bone deformities
- Masticatory disorders
- Chronic facial pain
- Aesthetic discomfort and low self-confidence
- Are in good health and have no contraindications to surgery
Advantages:
- Improved masticatory function
- Correction of malocclusion
- Facial harmonization
- Improved quality of life
- Increased self-confidence
Jaw reconstruction is a serious procedure that should be performed by a qualified and experienced maxillofacial surgeon.





























Name*
katana